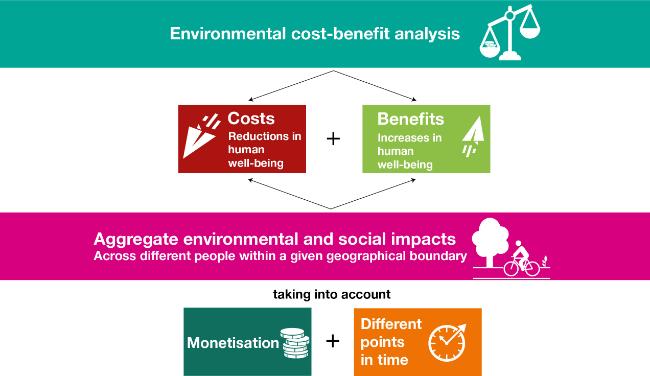
This provides greater visibility into the company’s spending over the year instead of merely showing how much it has received or paid out. Further, accounting has always been focused on objective data that can be accurately measured and evaluated without bias or opinion. The difference between these two statements is that the comprehensive statement provides information on how much cash reserves are available to cover future obligations and other commitments. It also includes information on its ability to raise funds through debt or equity markets and other sources. This phenomenon provides an interesting example of the trade-off between relevance and reliability in preparing financial data.
Going concern assumption is one of the fundamental assumptions in accounting on the basis of which financial statements are prepared. The historical cost principle states that virtually everything the company owns or controls (assets) must be recorded at its value at the date of acquisition. There are some exceptions to this rule, but always apply the cost principle unless the IFRS has specifically stated that a different valuation method should be used in a given circumstance. Therefore, total costs and expenses pertaining to the generation of such revenue together with the expenses and cost incurred for the specific accounting period are matched against the revenue for the said period. As such, Accrual System or Mercantile System of accounting is of fundamental importance in accounting. 1) Logical Approach – Accrual Concept ensures impact between revenue and cost whether it is received or not and paid or not.
2023 Global Survey Of Accounting Assumptions For Defined Benefit … – Mondaq News Alerts
2023 Global Survey Of Accounting Assumptions For Defined Benefit ….
Posted: Thu, 17 Aug 2023 16:02:27 GMT [source]
In addition, financial experts can generate safer and more accurate financial projections by overestimating expenses and underestimating revenues. The Accrual Basis of Accounting states that revenue and expenses are recorded when they are incurred, not necessarily when cash is exchanged. We’re not assuming that we’re going to go out of business this year or the next year.
1 Describe Principles, Assumptions, and Concepts of Accounting and Their Relationship to Financial Statements
We can say it is the logical thought of accounting which carries the process of preparation and finalization of Financial Statements. Additionally, adhering to these assumptions allows for more reliable data when making decisions regarding investments or acquisitions. In accounting, we assume that a company’s assets are equal to its liabilities plus the value of its equity. This means that assets will be recognized at an amount that is expected to be realized from its sale (net of selling costs) rather than from its continuing use in the ordinary course of the business.
Monetary UnitThe monetary unit assumption confers that activities that can be valued and measured in dollars are the only transactions to record. It also dictates that inflation not be considered as an adjustment at any Accounting Assumptions point. For instance, the FFSC dictates specific rules regarding how to record/measure assets on the balance sheet. Other specific examples would include how to value growing crops or high-value breeding livestock.
Defining Accounting Assumptions?
Inventory costing is an example of how the Matching Principle is applied in accounting practice. This accounting principle aims to ensure that all inventory-related expenses are matched with their related revenues so that the actual cost of goods sold can be accurately determined. The assumption is essential when creating financial statements and other forecasting and analysis documents.
Another key accounting assumption that persons working towards an accounting degree will need to understand is the going concern assumption. This assumption assumes that the business in question will likely continue operating in the foreseeable future. It assumes that the company will not go bankrupt and will be able to meet its obligations and objectives. The going concern assumption presumes that the business will be operating beyond its next fiscal period, will complete its expected plans, and meet its projected goals.
This way, users can understand the information correctly and make intelligent decisions about whether or not to invest in a company’s securities or debt offerings. Carl Menger, a German economist, published his groundbreaking book Principles of Economics in 1879, which introduced the concept of opportunity cost as a basis for economic decisions. The idea was expanded during the 1930s when John Maynard Keynes advanced his macroeconomic theories.
Accounting Assumptions for nonprofit organisations: a brief overview
There must be some form of objective evidence of a transaction before the business can report it in its accounting records. The principle of accrual states that profit or loss in an organisation should represent the activities of the enterprise and not the cash flows. As per the Indian Companies Act, the for-profit enterprises have a legal obligation to maintain the accounts on an accrual basis. Besides, this method helps to measure the income generated during the specific accounting period which also helps to distribute the same periodically. The accounting period concept recognises division and appropriation of accounting records into specific periods. Besides, under this concept, prepaid expenses are recognised as assets since the benefits will be utilised in future when the business entity will continue.
Accounting assumptions are the guidelines that accountants use when they prepare financial statements. They are used to ensure that the statements are in line with the law and other regulations. The periodicity (or time period) assumption implies that a company can divide its economic activities into artificial time periods. These time periods vary, but the most common are monthly, quarterly, and yearly. Though this legal assumption has not been extended to the sole trader and partnership business firms, for purposes of accounting, all transactions should specifically relate to the business operations of the entity itself.

An example of the Going Concern Assumption used in practice would be when a company prepares its financial statements for the year. Accountants will assume that the business will remain operational to create long-term plans and strategies. For instance, they may consider how much capital will be needed to support operations into the future, as well as project expected income based on sales and other sources of revenue.
Accounting Assumptions – Explained
For example, if an attorney is hired with an agreed
upon retainer fee of $2,500 in May, and the services are not performed until
July, the attorney does not recognize the revenue until July. The attorney must earn the income before it
can be recorded as such, even though he/she received cash for the service at an
earlier date. However, because the accrual method believes in recognising the income in advance, it can lead to an overstatement.
Going ForwardWhile the differences between the two accounting systems are basic, the sheer number of non-cash economic events that happen in a business are numerous, leading to a system that can be intimidating. It is worth it; any time more information is available, better decisions can be made. Analytics in both production and finance will result in more profit and greater success throughout the industry.
In Introduction to Financial Statements, we addressed the owner’s value in the firm as capital or owner’s equity. The primary reason for this distinction is that the typical company can have several to thousands of owners, and the financial statements for corporations require a greater amount of complexity. Recall that the accounting equation can be thought of from a “sources and claims” perspective; that is, the assets (items owned by the organization) were obtained by incurring liabilities or were provided by owners.
For example, an organization might use past sales data to assume future growth potential. Additionally, market conditions and customer demand can play a role in determining certain assumptions. These factors all work together to form the basis of an organization’s decision-making process regarding accounting and finance. The concept of assumptions in accounting has been around for centuries and is used to estimate financial information that may be difficult or impossible to quantify accurately.
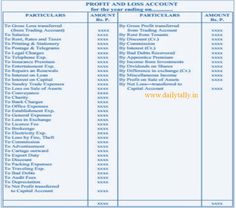
This becomes easier to understand as you become familiar with the normal balance of an account. The materiality principle relies on a professional’s judgment to determine whether transactions and transactional errors are material to the business. Errors may only sometimes have an impact on overall reporting or reporting accuracy. The conservatism assumption necessitates that professionals remain conservative in their reports and estimates. This can lead to more accurate record-keeping because accountants won’t risk producing overly optimized results.
The primary purpose of accounting assumptions is to maintain consistency and accuracy within financial records. By adhering to these principles, all companies can maintain accurate and comparable reporting standards, which enables stakeholders to compare one company’s financial performance with another’s. The assumption is vital in accounting, as it is the basis for all accounting principles. An assumption is an accepted fact used to draw conclusions and make decisions without proof or demonstration. Accounting assumptions provide the foundation for financial statements under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
A set of financial statements includes the income statement, statement of owner’s equity, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows. These statements are discussed in detail in Introduction to Financial Statements. This chapter explains the relationship between financial statements and several steps in the accounting process.
In addition, accounting assumptions are the foundation for recording assets, revenues, and expenses in financial statements such as the balance sheet and income statement. Such recognition may differ depending on the assumption, significantly impacting companies’ financial reporting practices. This is why accountants must thoroughly review their accounting assumptions to ensure that their financial statements accurately reflect their performance. An accounting assumption is a notion or opinion held by an accountant that isn’t always correct. Because of depreciation charges, an accountant may feel that a company’s assets will always be worth more than what they cost. Fundamental accounting assumptions or concepts are the set of assumptions that are made when preparing financial statements.
- It is a concept that can be defined as the degree to which one set of accounts or financial statements is identical.
- An example of the Accrual Basis of Accounting used in practice is when a company purchases equipment.
- This process allows for reliable financial statements to be created that accurately reflect the actual performance and profitability of the company during a period.
- In other words, organisations that are expected to continue are said to be a going concern.
Accounting is the business language used to evaluate performance and financial health. Despite their significance, accounting assumptions could be improved in many ways to prevent significant errors and poor decision-making. It refers to expectations and beliefs taken as accurate without proof or concrete evidence.

Leave a Reply